Green electricity is the term used to designate electricity produced solely from renewable sources such as hydraulic energy (e.g. dams, tides, waves), wind, solar, geothermal, or energy from biomass (wood, landfill gas, gas from wastewater treatment plants, biogas and more).
Energy Optimization
Since July 2014, lux-Airport has been supplied exclusively with green electricity via Enovos. The renewable energy certificates are issued by the Institut Luxembourgeois de Régulation (ILR) and also validated by the European Energy Certification System (EECS). Our electricity mainly comes from hydraulic energy. Since 2020, the gas used to heat the terminals has also been climate-neutral.
Nevertheless, energy is too precious to be wasted, even if it comes from renewable sources. For this reason, after a general audit, we are currently working to optimize the use of energy in terminals A and B. Several projects were already carried out in 2021, such as replacing the energy meters (hot/cold), revising the set points, and replacing part of the lighting with LED. In 2022, optimizations and adjustments continued with new parameters implemented for public and office areas, which allow some temperature variations, but significantly reduce overall energy consumption. For instance, in the offices, the air conditioning will start cooling only when the temperature reaches 24° according to the thermostat setting. In 2023, this measure, among many others, will help us to reduce the energy consumption for heating the terminal by more than 50% and for cooling by more than 30%. This system will be monitored, analyzed and adjusted further during the coming months and seasons in order to bolster the overall effort required as much as we can.
Led Dimming at Underground Parking
The car parks used to remain lit 24/7, resulting in high energy consumption and high operating costs. We had to balance two issues: remaining consistent with our overall approach to reducing environmental impacts while ensuring the safety of pedestrians and drivers. Approximately 5,500 lights and 1,500 emergency lights were replaced with new LED lights, offering a better quality of lighting with a longer life span. These LED lights are “smart” because they are coupled to presence detectors, which allow the lights to dim the light in areas where there are no users and turn them up to maximum brightness instantly. For this work, we have been able to save more than 750,000kWh since installing the new lighting, which is equivalent to a 35% reduction in the overall electricity consumption of the car park.

GUARANTEES OF ORIGIN
An electricity supply offer is said to be “green” if the supplier can guarantee that a quantity of electricity of renewable origin equivalent to the consumption of the customers of this offer has been injected into the network. To prove this, only the Guarantees of Origin (GO) have certification value.
Guarantees of Origin ensure, at the European level, the administrative traceability of green electricity. These are electronic certificates issued to producers in proportion to the quantity of electricity produced from renewable energy sources.
HYDROELECTRIC POWER PLANTS
| 17 | 3 | 2014 |
|---|---|---|
| POWER PLANTS IN NORWAY | POWER PLANTS IN ICELAND | EVER SINCE EXCLUSIVELY GREEN POWER SUPPLY |
Our electricity comes mainly from hydraulic energy. This energy includes the energy provided by the movement of water in all its forms: waterfalls, rivers, ocean currents, tides, waves. Hydraulic (mechanical) energy is converted into electrical energy in hydroelectric power plants. This renewable electricity is used not only to light the terminals, runway and aprons, but also to recharge the site’s electric vehicles and to supply energy to the aircraft in transit.

Depending on the supplier and the year, electrical energy is produced in countries that have a surplus of electricity production:
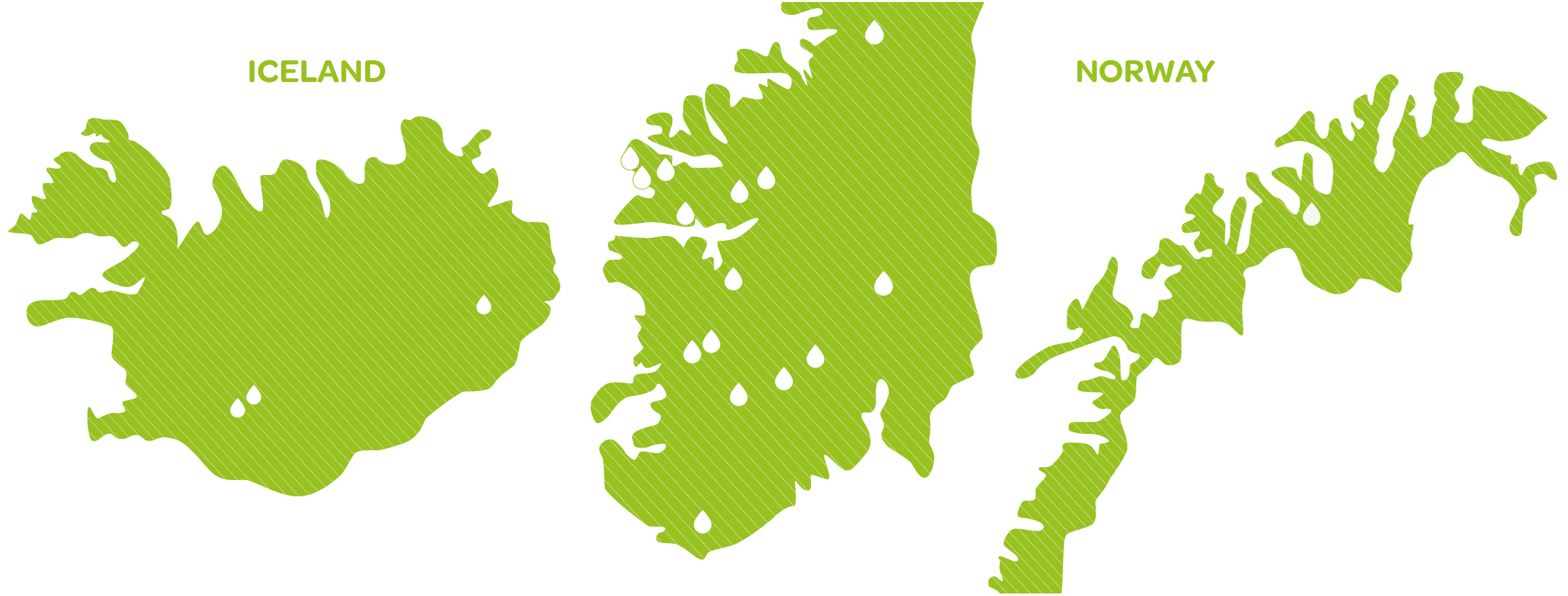
- Iceland: at Búrfellsstöð (2019), Fljótdalsstöð (2020, 2018), Sultartangastöð (2021). These power plants use the force of water movement from dams and the force of the water movement of several lakes and rivers.
- Norway: at Nes (2021), Kvænangsbotn (2019), Sagefossen (2017), Svelgen (2017), Øksenelvane (2017, 2016), Leirdøla (2016), Makkoren (2016), Åskåra (2016), Mageli (2016), Oksla (2015). Tokke (2015), Jostedal (2015), Aurland (2015), Svorkmo (2015), Mår (2014) and Nore (2014). These power plants use the force of water movement from several lakes and rivers.
ELECTRICITY AND CO2
The use of electricity by the consumer does not result in direct greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions at the point of use. However, the use of fuels to generate electricity and to build and maintain its transmission and distribution networks do result in various GHG emissions.
The release of greenhouse gases (GHG) into the atmosphere depends mainly on the activity and the process of electricity production. Depending on the different production methods, to estimate the GHG emissions per unit of electrical energy (kWh), there are internationally and European recognized factors called emission factors (EF).
An emission factor is a coefficient used to convert activity data into GHG emissions, which corresponds to the average emission rate of a given source expressed in kg of CO2 per kWh. For any production of electrical energy using renewable primary energy (wind, solar, wood, geothermal, etc.), this factor is 0. As an example, this rate is 0.215 kg CO2 /kWh for the electric mix in Luxembourg and it increases to 2.58 kg CO2 /kWh for the diesel used in cars. This rate increases to 0.461 kg CO2 /kWh in Germany because of the use of fossil fuels to produce electricity.
Emissions related to the manufacture and maintenance of the generating device are accounted for in the energy producer’s carbon footprint. The use of renewable electrical energy is therefore considered emission-free.
WHAT DOES CO2EQ MEAN?

A human activity emits different types of greenhouse gases (GHG). Their global warming potential (GWP), which is a physical characteristic of GHGs, represents their impact on the greenhouse effect and allows us to convert 1 kg of GHG into X kg of CO2 equivalent, noted CO2eq. In this way, the emissions of different gases can be compared.